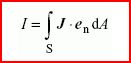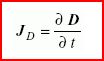-
1 ток проводимости
ток проводимости
Явление направленного движения свободных носителей электрического заряда в веществе или в пустоте, количественно характеризуемое скалярной величиной, равной производной по времени от электрического заряда, переносимого свободными носителями заряда сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
(electric) current
(conduction) current
scalar quantity equal to the flux of the electric current density J through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE 1 – The electric current through a surface is equal to the limit of the quotient of the electric charge transferred through that surface during a time interval by the duration of this interval when this duration tends to zero.
NOTE 2 – For charge carriers confined to a surface, the electric current is defined through a curve of this surface (see the note to term “lineic electric current”).
[IEV number 121-11-13]FR
courant (électrique), m
courant (de conduction), m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant électrique J à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE 1 – Le courant électrique à travers une surface est égal à la limite du quotient de la charge électrique traversant cette surface pendant un intervalle de temps par la durée de cet intervalle lorsque cette durée tend vers zéro.
NOTE 2 – Pour des porteurs de charge confinés sur une surface, le courant électrique est défini à travers une courbe de cette surface (voir la note au terme "densité linéique de courant").
[IEV number 121-11-13]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- (elektrische) Stromstärke
- Leitungsstromstärke
- Stromstärke, (elektrische)
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > ток проводимости
-
2 ток проводимости
- Stromstärke, (elektrische)
- Leitungsstromstärke
- (elektrische) Stromstärke
ток проводимости
Явление направленного движения свободных носителей электрического заряда в веществе или в пустоте, количественно характеризуемое скалярной величиной, равной производной по времени от электрического заряда, переносимого свободными носителями заряда сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
(electric) current
(conduction) current
scalar quantity equal to the flux of the electric current density J through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE 1 – The electric current through a surface is equal to the limit of the quotient of the electric charge transferred through that surface during a time interval by the duration of this interval when this duration tends to zero.
NOTE 2 – For charge carriers confined to a surface, the electric current is defined through a curve of this surface (see the note to term “lineic electric current”).
[IEV number 121-11-13]FR
courant (électrique), m
courant (de conduction), m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant électrique J à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE 1 – Le courant électrique à travers une surface est égal à la limite du quotient de la charge électrique traversant cette surface pendant un intervalle de temps par la durée de cet intervalle lorsque cette durée tend vers zéro.
NOTE 2 – Pour des porteurs de charge confinés sur une surface, le courant électrique est défini à travers une courbe de cette surface (voir la note au terme "densité linéique de courant").
[IEV number 121-11-13]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- (elektrische) Stromstärke
- Leitungsstromstärke
- Stromstärke, (elektrische)
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > ток проводимости
-
3 ток проводимости
ток проводимости
Явление направленного движения свободных носителей электрического заряда в веществе или в пустоте, количественно характеризуемое скалярной величиной, равной производной по времени от электрического заряда, переносимого свободными носителями заряда сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
(electric) current
(conduction) current
scalar quantity equal to the flux of the electric current density J through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE 1 – The electric current through a surface is equal to the limit of the quotient of the electric charge transferred through that surface during a time interval by the duration of this interval when this duration tends to zero.
NOTE 2 – For charge carriers confined to a surface, the electric current is defined through a curve of this surface (see the note to term “lineic electric current”).
[IEV number 121-11-13]FR
courant (électrique), m
courant (de conduction), m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant électrique J à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE 1 – Le courant électrique à travers une surface est égal à la limite du quotient de la charge électrique traversant cette surface pendant un intervalle de temps par la durée de cet intervalle lorsque cette durée tend vers zéro.
NOTE 2 – Pour des porteurs de charge confinés sur une surface, le courant électrique est défini à travers une courbe de cette surface (voir la note au terme "densité linéique de courant").
[IEV number 121-11-13]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- (elektrische) Stromstärke
- Leitungsstromstärke
- Stromstärke, (elektrische)
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > ток проводимости
-
4 плотность тока
1) Engineering: ampere density, current density (электрического)2) Chemistry: conductance3) Railway term: current intensity, current per square centimeter4) Automobile industry: charge density (при зарядке аккумулятора), intensity of current5) Metallurgy: current density (эмиссии)6) Makarov: electric current density7) Electrochemistry: vapour density -
5 электромагнитное поле
электромагнитное поле
Вид материи, определяемый во всех точках двумя векторными величинами, которые характеризуют две его стороны, называемые «электрическое поле» и «магнитное поле», оказывающий силовое воздействие на электрически заряженные частицы, зависящее от их скорости и электрического заряда.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
electromagnetic field
field, determined by a set of four interrelated vector quantities, that characterizes, together with the electric current density and the volumic electric charge, the electric and magnetic conditions of a material medium or of vacuum
NOTE 1 – The four interrelated vector quantities, which obey Maxwell equations, are by convention:
– the electric field strength E,
– the electric flux density D,
– the magnetic field strength H,
– the magnetic flux density B.
NOTE 2 – This definition of electromagnetic field is valid in so far as certain quantum aspects of electromagnetic phenomena can be neglected.
Source: from 705-01-07
[IEV number 121-11-61]FR
champ électromagnétique, m
champ, déterminé par un ensemble de quatre grandeurs vectorielles reliées entre elles, qui caractérise, avec la densité de courant électrique et la charge électrique volumique, les états électrique et magnétique d'un milieu matériel ou du vide
NOTE 1 – Les quatre grandeurs vectorielles reliées entre elles, qui vérifient les équations de Maxwell, sont par convention:
– le champ électrique E,
– l'induction électrique D,
– le champ magnétique H,
– l'induction magnétique B.
NOTE 2 – Cette définition du champ électromagnétique est valable dans la mesure où certains des aspects quantiques des phénomènes électromagnétiques peuvent être négligés.
Source: d'après 705-01-07
[IEV number 121-11-61]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > электромагнитное поле
-
6 электромагнитное поле
электромагнитное поле
Вид материи, определяемый во всех точках двумя векторными величинами, которые характеризуют две его стороны, называемые «электрическое поле» и «магнитное поле», оказывающий силовое воздействие на электрически заряженные частицы, зависящее от их скорости и электрического заряда.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
electromagnetic field
field, determined by a set of four interrelated vector quantities, that characterizes, together with the electric current density and the volumic electric charge, the electric and magnetic conditions of a material medium or of vacuum
NOTE 1 – The four interrelated vector quantities, which obey Maxwell equations, are by convention:
– the electric field strength E,
– the electric flux density D,
– the magnetic field strength H,
– the magnetic flux density B.
NOTE 2 – This definition of electromagnetic field is valid in so far as certain quantum aspects of electromagnetic phenomena can be neglected.
Source: from 705-01-07
[IEV number 121-11-61]FR
champ électromagnétique, m
champ, déterminé par un ensemble de quatre grandeurs vectorielles reliées entre elles, qui caractérise, avec la densité de courant électrique et la charge électrique volumique, les états électrique et magnétique d'un milieu matériel ou du vide
NOTE 1 – Les quatre grandeurs vectorielles reliées entre elles, qui vérifient les équations de Maxwell, sont par convention:
– le champ électrique E,
– l'induction électrique D,
– le champ magnétique H,
– l'induction magnétique B.
NOTE 2 – Cette définition du champ électromagnétique est valable dans la mesure où certains des aspects quantiques des phénomènes électromagnétiques peuvent être négligés.
Source: d'après 705-01-07
[IEV number 121-11-61]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > электромагнитное поле
-
7 электромагнитное поле
электромагнитное поле
Вид материи, определяемый во всех точках двумя векторными величинами, которые характеризуют две его стороны, называемые «электрическое поле» и «магнитное поле», оказывающий силовое воздействие на электрически заряженные частицы, зависящее от их скорости и электрического заряда.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
electromagnetic field
field, determined by a set of four interrelated vector quantities, that characterizes, together with the electric current density and the volumic electric charge, the electric and magnetic conditions of a material medium or of vacuum
NOTE 1 – The four interrelated vector quantities, which obey Maxwell equations, are by convention:
– the electric field strength E,
– the electric flux density D,
– the magnetic field strength H,
– the magnetic flux density B.
NOTE 2 – This definition of electromagnetic field is valid in so far as certain quantum aspects of electromagnetic phenomena can be neglected.
Source: from 705-01-07
[IEV number 121-11-61]FR
champ électromagnétique, m
champ, déterminé par un ensemble de quatre grandeurs vectorielles reliées entre elles, qui caractérise, avec la densité de courant électrique et la charge électrique volumique, les états électrique et magnétique d'un milieu matériel ou du vide
NOTE 1 – Les quatre grandeurs vectorielles reliées entre elles, qui vérifient les équations de Maxwell, sont par convention:
– le champ électrique E,
– l'induction électrique D,
– le champ magnétique H,
– l'induction magnétique B.
NOTE 2 – Cette définition du champ électromagnétique est valable dans la mesure où certains des aspects quantiques des phénomènes électromagnétiques peuvent être négligés.
Source: d'après 705-01-07
[IEV number 121-11-61]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > электромагнитное поле
-
8 плотность электрического тока
1) Electronics: current density2) Makarov: electric current densityУниверсальный русско-английский словарь > плотность электрического тока
-
9 полная плотность электрического тока
Electronics: total electric-current densityУниверсальный русско-английский словарь > полная плотность электрического тока
-
10 явление электрической дуги
явление электрической дуги
-
[Интент]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Electric arc phenomenon
The electric arc is a phenomenon which takes place as a consequence of a discharge which occurs when the voltage between two points exceeds the insulating strength limit of the interposed gas; then, in the presence of suitable conditions, a plasma is generated which carries the electric current till the opening of the protective device on the supply side.
Gases, which are good insulating means under normal conditions, may become current conductors in consequence of a change in their chemical-physical properties due to a temperature rise or to other external factors.
To understand how an electrical arc originates, reference can be made to what happens when a circuit opens or closes.
During the opening phase of an electric circuit the contacts of the protective device start to separate thus offering to the current a gradually decreasing section; therefore the current meets growing resistance with a consequent rise in the temperature.
As soon as the contacts start to separate, the voltage applied to the circuit exceeds the dielectric strength of the air, causing its perforation through a discharge.
The high temperature causes the ionization of the surrounding air which keeps the current circulating in the form of electrical arc. Besides thermal ionization, there is also an electron emission from the cathode due to the thermionic effect; the ions formed in the gas due to the very high temperature are accelerated by the electric field, strike the cathode, release energy in the collision thus causing a localized heating which generates electron emission.
The electrical arc lasts till the voltage at its ends supplies the energy sufficient to compensate for the quantity of heat dissipated and to maintain the suitable conditions of temperature. If the arc is elongated and cooled, the conditions necessary for its maintenance lack and it extinguishes.
Analogously, an arc can originate also as a consequence of a short-circuit between phases. A short-circuit is a low impedance connection between two conductors at different voltages.
The conducting element which constitutes the low impedance connection (e.g. a metallic tool forgotten on the busbars inside the enclosure, a wrong wiring or a body of an animal entered inside the enclosure), subject to the difference of potential is passed through by a current of generally high value, depending on the characteristics of the circuit.
The flow of the high fault current causes the overheating of the cables or of the circuit busbars, up to the melting of the conductors of lower section; as soon as the conductor melts, analogous conditions to those present during the circuit opening arise. At that point an arc starts which lasts either till the protective devices intervene or till the conditions necessary for its stability subsist.
The electric arc is characterized by an intense ionization of the gaseous means, by reduced drops of the anodic and cathodic voltage (10 V and 40 V respectively), by high or very high current density in the middle of the column (of the order of 102-103 up to 107 A/cm2), by very high temperatures (thousands of °C) always in the middle of the current column and – in low voltage - by a distance between the ends variable from some microns to some centimeters.
[ABB]Явление электрической дуги
Электрическая дуга между двумя электродами в газе представляет собой физическое явление, возникающее в тот момент, когда напряжения между двумя электродами превышает значение электрической прочности изоляции данного газа.
При наличии подходящих условий образуется плазма, по которой протекает электрический ток. Ток будет протекать до тех пор, пока на стороне электропитания не сработает защитное устройство.
Газы, являющиеся хорошим изолятором, при нормальных условиях, могут стать проводником в результате изменения их физико-химических свойств, которые могут произойти вследствие увеличения температуры или в результате воздействия каких-либо иных внешних факторов.
Для того чтобы понять механизм возникновения электрической дуги, следует рассмотреть, что происходит при размыкании или замыкании электрической цепи.
При размыкании электрической цепи контакты защитного устройства начинают расходиться, в результате чего постепенно уменьшается сечение контактной поверхности, через которую протекает ток.
Сопротивление электрической цепи возрастает, что приводит к увеличению температуры.
Как только контакты начнут отходить один от другого, приложенное напряжение превысит электрическую прочность воздуха, что вызовет электрический пробой.
Высокая температура приведет к ионизации воздуха, которая обеспечит протекание электрического тока по проводнику, представляющему собой электрическую дугу. Кроме термической ионизации молекул воздуха происходит также эмиссия электронов с катода, вызванная термоэлектронным эффектом. Образующиеся под воздействием очень высокой температуры ионы ускоряются в электрическом поле и бомбардируют катод. Высвобождающаяся, в результате столкновения энергия, вызывает локальный нагрев, который, в свою очередь, приводит к эмиссии электронов.
Электрическая дуга длится до тех пор, пока напряжение на ее концах обеспечивает поступление энергии, достаточной для компенсации выделяющегося тепла и для сохранения условий поддержания высокой температуры. Если дуга вытягивается и охлаждается, то условия, необходимые для ее поддержания, исчезают и дуга гаснет.
Аналогичным образом возникает дуга в результате короткого замыкания электрической цепи. Короткое замыкание представляет собой низкоомное соединение двух проводников, находящихся под разными потенциалами.
Проводящий элемент с малым сопротивлением, например, металлический инструмент, забытый на шинах внутри комплектного устройства, ошибка в электромонтаже или тело животного, случайно попавшего в комплектное устройство, может соединить элементы, находящиеся под разными потенциалами, в результате чего через низкоомное соединение потечет электрический ток, значение которого определяется параметрами образовавшейся короткозамкнутой цепи.
Протекание большого тока короткого замыкания вызывает перегрев кабелей или шин, который может привести к расплавлению проводников с меньшим сечением. Как только проводник расплавится, возникает ситуация, аналогичная размыканию электрической цепи. Т. е. в момент размыкания возникает дуга, которая длится либо до срабатывания защитного устройства, либо до тех пор, пока существуют условия, обеспечивающие её стабильность.
Электрическая дуга характеризуется интенсивной ионизацией газов, что приводит к падению анодного и катодного напряжений (на 10 и 40 В соответственно), высокой или очень высокой плотностью тока в середине плазменного шнура (от 102-103 до 107 А/см2), очень высокой температурой (сотни градусов Цельсия) всегда в середине плазменного шнура и низкому падению напряжения при расстоянии между концами дуги от нескольких микрон до нескольких сантиметров.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > явление электрической дуги
-
11 плотность тока смещения
density of displacement current, electric displacement current densityРусско-английский словарь по электронике > плотность тока смещения
-
12 плотность тока смещения
density of displacement current, electric displacement current densityРусско-английский словарь по радиоэлектронике > плотность тока смещения
-
13 ток
ток
Скалярная величина, равная сумме электрического тока проводимости, электрического тока переноса и электрического тока смещения сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
total electric current
scalar quantity given by the flux of the total current density Jt through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE – The total electric current It is given by
It = I + ID
where I is the electric current and ID the displacement current.
[IEV number 121-11-45]FR
courant électrique total, m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant total Jt à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE – Le courant électrique total It est donné par
It = I + ID
où I est le courant électrique et ID le courant de déplacement.
[IEV number 121-11-45]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Действия
- включать ток
- длительно пропускать ток
- коммутировать ток
- ограничивать ток
- отключать ток
- потреблять ток
- проводить ток
- пропускать ток
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > ток
-
14 ток
ток
Скалярная величина, равная сумме электрического тока проводимости, электрического тока переноса и электрического тока смещения сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
total electric current
scalar quantity given by the flux of the total current density Jt through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE – The total electric current It is given by
It = I + ID
where I is the electric current and ID the displacement current.
[IEV number 121-11-45]FR
courant électrique total, m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant total Jt à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE – Le courant électrique total It est donné par
It = I + ID
où I est le courant électrique et ID le courant de déplacement.
[IEV number 121-11-45]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Действия
- включать ток
- длительно пропускать ток
- коммутировать ток
- ограничивать ток
- отключать ток
- потреблять ток
- проводить ток
- пропускать ток
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > ток
-
15 ток
ток
Скалярная величина, равная сумме электрического тока проводимости, электрического тока переноса и электрического тока смещения сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
total electric current
scalar quantity given by the flux of the total current density Jt through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE – The total electric current It is given by
It = I + ID
where I is the electric current and ID the displacement current.
[IEV number 121-11-45]FR
courant électrique total, m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant total Jt à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE – Le courant électrique total It est donné par
It = I + ID
où I est le courant électrique et ID le courant de déplacement.
[IEV number 121-11-45]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Действия
- включать ток
- длительно пропускать ток
- коммутировать ток
- ограничивать ток
- отключать ток
- потреблять ток
- проводить ток
- пропускать ток
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > ток
-
16 плотность тока смещения
плотность тока смещения JD
Векторная величина, равная производной по времени от электрического смещения.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
displacement current density
vector quantity equal to the time derivative of the electric flux density D:
[IEV number 121-11-42]FR
densité de courant de déplacement, f
grandeur vectorielle égale à la dérivée par rapport au temps de l'induction électrique D:
[IEV number 121-11-42]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > плотность тока смещения
-
17 плотность тока смещения
1) Engineering: displacement current density2) Electronics: density of displacement current3) Makarov: electric displacement current densityУниверсальный русско-английский словарь > плотность тока смещения
-
18 плотность тока смещения
плотность тока смещения JD
Векторная величина, равная производной по времени от электрического смещения.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
displacement current density
vector quantity equal to the time derivative of the electric flux density D:
[IEV number 121-11-42]FR
densité de courant de déplacement, f
grandeur vectorielle égale à la dérivée par rapport au temps de l'induction électrique D:
[IEV number 121-11-42]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > плотность тока смещения
-
19 плотность тока смещения
плотность тока смещения JD
Векторная величина, равная производной по времени от электрического смещения.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
displacement current density
vector quantity equal to the time derivative of the electric flux density D:
[IEV number 121-11-42]FR
densité de courant de déplacement, f
grandeur vectorielle égale à la dérivée par rapport au temps de l'induction électrique D:
[IEV number 121-11-42]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > плотность тока смещения
-
20 плотность электрического тока смещения
1) Electronics: density of displacement current2) Makarov: electric displacement current densityУниверсальный русско-английский словарь > плотность электрического тока смещения
- 1
- 2
См. также в других словарях:
electric current density — elektros srovės tankis statusas T sritis Standartizacija ir metrologija apibrėžtis Apibrėžtį žr. priede. priedas( ai) Grafinis formatas atitikmenys: angl. areic electric current; electric current density vok. elektrische Stromdichte, f rus.… … Penkiakalbis aiškinamasis metrologijos terminų žodynas
electric current density — elektros srovės tankis statusas T sritis Standartizacija ir metrologija apibrėžtis Elektros srovės stipris vienetiniame plote. Matavimo vienetas: A/m². atitikmenys: angl. areic electric current; electric current density vok. elektrische… … Penkiakalbis aiškinamasis metrologijos terminų žodynas
electric current density — elektros srovės tankis statusas T sritis Standartizacija ir metrologija apibrėžtis Vektorius, kurio skaitinė vertė lygi krūviui, pereinančiam per vienetinį laiko tarpą per vienetinio ploto paviršių, statmeną elektringųjų dalelių (krūvininkų)… … Penkiakalbis aiškinamasis metrologijos terminų žodynas
electric current density — elektros srovės tankis statusas T sritis fizika atitikmenys: angl. electric current density vok. elektrische Stromdichte, f rus. плотность электрического тока, f pranc. densité de courant électrique, f … Fizikos terminų žodynas
linear electric current density — ilginis elektros srovės tankis statusas T sritis Standartizacija ir metrologija apibrėžtis Laidžiąja juostele tekančios elektros srovės stipris, padalytas iš tos juostelės pločio. Matavimo vienetas: A/m. atitikmenys: angl. linear electric current … Penkiakalbis aiškinamasis metrologijos terminų žodynas
linear electric current density — ilginis elektros srovės tankis statusas T sritis fizika atitikmenys: angl. linear electric current density vok. Linienstromdichte, f rus. линейная плотность электрического тока, f pranc. densité linéaire de courant électrique, f … Fizikos terminų žodynas
Current density — This page is about the electric current density in electromagnetism. For the probability current density in quantum mechanics, see Probability current. Current density is a measure of the density of flow of a conserved charge. Usually the charge… … Wikipedia
current density — n. the amount of electric current passing through a cross sectional area (perpendicular to the direction of current) of a conductor in a given unit of time: commonly expressed in amperes per square centimeter or amperes per square inch … English World dictionary
Electric current — Electromagnetism … Wikipedia
current density — noun : the current per unit area of cross section perpendicular to flow in a region through which an electric current is flowing … Useful english dictionary
areic electric current — elektros srovės tankis statusas T sritis Standartizacija ir metrologija apibrėžtis Apibrėžtį žr. priede. priedas( ai) Grafinis formatas atitikmenys: angl. areic electric current; electric current density vok. elektrische Stromdichte, f rus.… … Penkiakalbis aiškinamasis metrologijos terminų žodynas